Robot-Native Fulfillment Providers: A Cost Comparison Guide for E-Commerce Shippers in 2026

The warehouse automation market is on track to exceed $90 billion by 2033 — a 329% increase over a decade — and a new breed of fulfillment provider is emerging at the center of that growth. Robot-native 3PLs don't retrofit automation into legacy warehouses. They build facilities around robots from day one, promising lower per-unit costs, faster throughput, and SLA-backed delivery speeds that traditional providers struggle to match.
For e-commerce shippers evaluating their fulfillment strategy in 2026, the question is no longer whether to use automation — it's whether to partner with a provider that was born automated.
What "Robot-Native" Actually Means
Traditional 3PLs add automation incrementally: a conveyor belt here, a pick-assist robot there, layered onto workflows designed for human labor. Robot-native providers flip that model. Their facilities are engineered around autonomous mobile robots (AMRs), AI-driven orchestration, and goods-to-person systems from the ground up.
The distinction matters for cost structure. Retrofitted automation creates hybrid workflows where humans and robots share space, often requiring complex integration and safety protocols. Robot-native facilities eliminate that friction, achieving higher pick density and lower cost per order because every process was designed for machines first.
According to Modern Materials Handling's 2026 Automation Study, only 12% of warehouses report fully automated picking today — meaning robot-native providers occupy a still-rare competitive position. Companies plan to spend an average of $1.6 million on automation in 2026, up from $1.5 million in 2025, as the pressure to modernize intensifies.
The Provider Landscape: Who's Robot-Native?
Not every 3PL claiming automation qualifies as robot-native. Here's how the key players stack up:
Nimble operates fully autonomous fulfillment centers across three U.S. locations, with $115 million in funding behind its AI-powered robotic systems. Their pitch: 2-day delivery to 78%+ of the U.S. included in standard pricing, with no upfront investment required from brands. Nimble's robots handle picking, packing, and sorting end-to-end, targeting standard e-commerce products like apparel, health and beauty, footwear, and electronics.
ShipMonk runs 12 fulfillment centers across the U.S., Canada, and Europe with significant robotic automation investment. While not fully autonomous like Nimble, ShipMonk's technology-driven approach includes robotic pick-assist systems and automated sortation. They're strongest for subscription box fulfillment and crowdfunding campaigns.
Quiet Logistics (now part of Shopify Logistics) pioneered the use of Locus Robotics AMRs in fulfillment warehouses, with goods-to-person systems that reduce picker walk time by up to 50%. Their integration with Shopify's ecosystem makes them a natural choice for brands already on that platform.
Tompkins Robotics offers a modular approach — their t-Sort robotic sortation system can scale from startup volumes to enterprise throughput. Rather than operating as a traditional 3PL, Tompkins provides robotic infrastructure that other fulfillment providers deploy, making them a behind-the-scenes enabler.
Cost Structure Comparison
The economics of robot-native fulfillment differ fundamentally from traditional 3PLs. Here's what shippers need to evaluate:
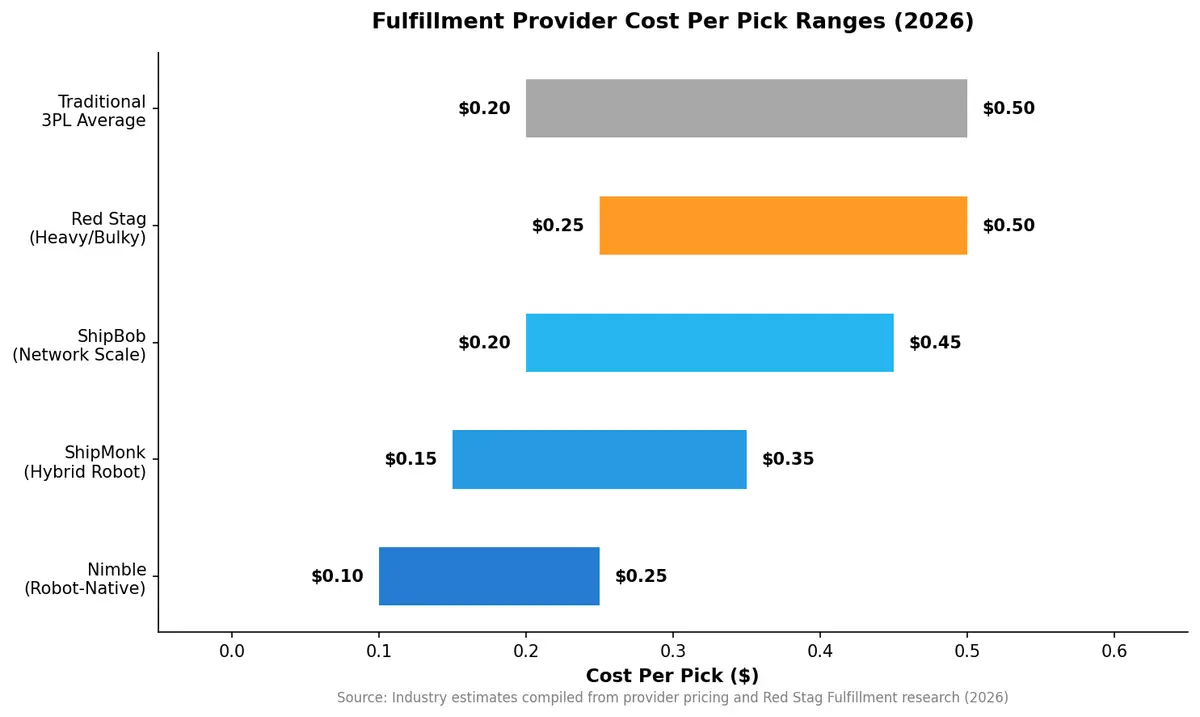
Per-pick fees are where robot-native providers show their advantage. Traditional 3PLs typically charge $0.20–$0.50 per pick depending on complexity and volume. Robot-native providers push that lower through automation density — Nimble bundles 2-day shipping into their per-unit pricing, effectively eliminating separate pick-and-pack line items for standard orders.
Storage costs remain comparable across provider types, typically ranging from $0.50–$1.50 per cubic foot per month. Robot-native facilities can store more densely (goods-to-person systems don't need wide aisles for human pickers), but savings vary by SKU profile.
Shipping bundling is the key differentiator. Traditional 3PLs pass through carrier rates, meaning shippers negotiate separately or accept the 3PL's negotiated rates. Robot-native providers like Nimble include delivery in their pricing model — a structural advantage that simplifies cost forecasting and often reduces total landed cost.
Minimum volume requirements vary significantly. ShipMonk and traditional 3PLs often work with lower minimums, while fully automated facilities need consistent volume to maintain efficiency. Brands shipping fewer than 1,000 orders per month may find traditional providers more flexible.
When Robot-Native Makes Sense
Robot-native fulfillment isn't universally the right choice. It excels in specific scenarios:
High-volume, standard products. If you're shipping 5,000+ orders per month of standard-sized items (apparel, supplements, electronics accessories), robot-native providers deliver the best unit economics. Their automation is optimized for predictable, repeatable workflows.
Speed-sensitive brands. DHL's autonomous innovations have accelerated processes at 95% of its global warehouses, with item-picking robots increasing units picked per hour by 30%, according to CNBC's reporting on warehouse automation. Robot-native 3PLs deliver similar throughput gains — critical for brands competing on delivery speed.
Seasonal scalability. Robot-native facilities handle demand spikes without the hiring and training lag that plagues traditional warehouses. When UPS processes 68% of U.S. volume through automated facilities in 2026, up from 66.5% in 2025, the industry signal is clear: automation handles volatility better than labor alone.
When traditional 3PLs still win: Heavy, oversized, or fragile items that require specialized handling. Complex kitting operations. Low-volume brands needing flexible minimums. Products requiring FDA-registered or temperature-controlled storage.
Integration Requirements
Switching to a robot-native fulfillment provider isn't just a logistics decision — it's a systems integration project. Most robot-native 3PLs offer standard integrations with Shopify, WooCommerce, Amazon, and other major platforms, but the real complexity emerges in:
- Inventory synchronization across multiple sales channels and fulfillment locations
- Order routing logic that determines which facility handles each order based on proximity, inventory availability, and SLA requirements
- Returns processing workflows that feed back into automated inventory management
- Real-time visibility into robotic fulfillment status for customer-facing tracking
This is where a TMS platform becomes essential. Connecting your order management, carrier network, and fulfillment providers into a single orchestration layer eliminates the data silos that create shipping errors and cost overruns.
The Bottom Line for 2026
The fulfillment market is splitting into two lanes. Traditional 3PLs will continue serving complex, specialized, and lower-volume operations. Robot-native providers will capture an increasing share of standard e-commerce fulfillment, driven by lower unit costs, faster throughput, and SLA guarantees that human-dependent operations can't match.
For shippers evaluating the switch, the decision framework is straightforward: calculate your current cost-per-order (including pick, pack, ship, and error costs), compare it against robot-native provider quotes, and factor in the speed and accuracy improvements that automation delivers.
The $90 billion question isn't whether warehouse automation will become standard — it's whether your fulfillment partner was built for it from the start.
Ready to connect your fulfillment network into a unified logistics platform? Contact CXTMS for a demo and see how intelligent TMS orchestration bridges the gap between your e-commerce operations and automated fulfillment providers.


